Water-soluble fiber plays a crucial role in reducing cholesterol levels by binding to bile acids in the digestive system, effectively lowering LDL cholesterol. Common sources include oats, beans, fruits, and vegetables. To effectively add fiber to your diet, incorporate high-fiber breakfasts, choose healthy snacks, and gradually increase your intake while staying hydrated.
Water-soluble fiber plays a crucial role in reducing cholesterol levels, promoting heart health, and improving digestion. This type of fiber dissolves in water, forming a gel-like substance that helps to lower LDL cholesterol, commonly known as bad cholesterol. In this article, we’ll explore the mechanisms by which water-soluble fiber aids in cholesterol reduction, identify some of the best dietary sources, and provide tips on how to incorporate more fiber into your daily meals.
Understanding Water-Soluble Fiber

Understanding water-soluble fiber is essential to knowing how it impacts our health. Unlike insoluble fiber, which adds bulk to stool and helps food pass through the digestive tract, water-soluble fiber dissolves in water, forming a gel-like substance. This unique property allows it to bind with substances in the digestive system, particularly cholesterol.
What is Water-Soluble Fiber?
Water-soluble fiber is a type of dietary fiber found in various foods, including fruits, vegetables, beans, and oats. It can help lower bad cholesterol (LDL) levels, control blood sugar levels, and support overall digestive health.
How Does It Work?
When water-soluble fiber is ingested, it absorbs water and expands. This gel-like consistency slows down digestion, leading to a steadier release of glucose into the bloodstream and preventing spikes in blood sugar after meals. Additionally, as the fiber passes through the intestines, it binds to cholesterol, which is then excreted instead of being absorbed into the bloodstream.
Importance of Increasing Fiber Intake
Incorporating water-soluble fiber into your diet is important for heart health. Studies show that a high-fiber diet can reduce the risk of heart disease. Consuming adequate fiber can also promote satiety, helping with weight management.
To reap the health benefits, aim for a variety of sources of water-soluble fiber. This could be achieved by enjoying a bowl of oatmeal in the morning, snacking on fruits like apples and oranges, or adding beans to salads. Each food source brings unique nutrients and benefits!
How Fiber Lowers Cholesterol Levels
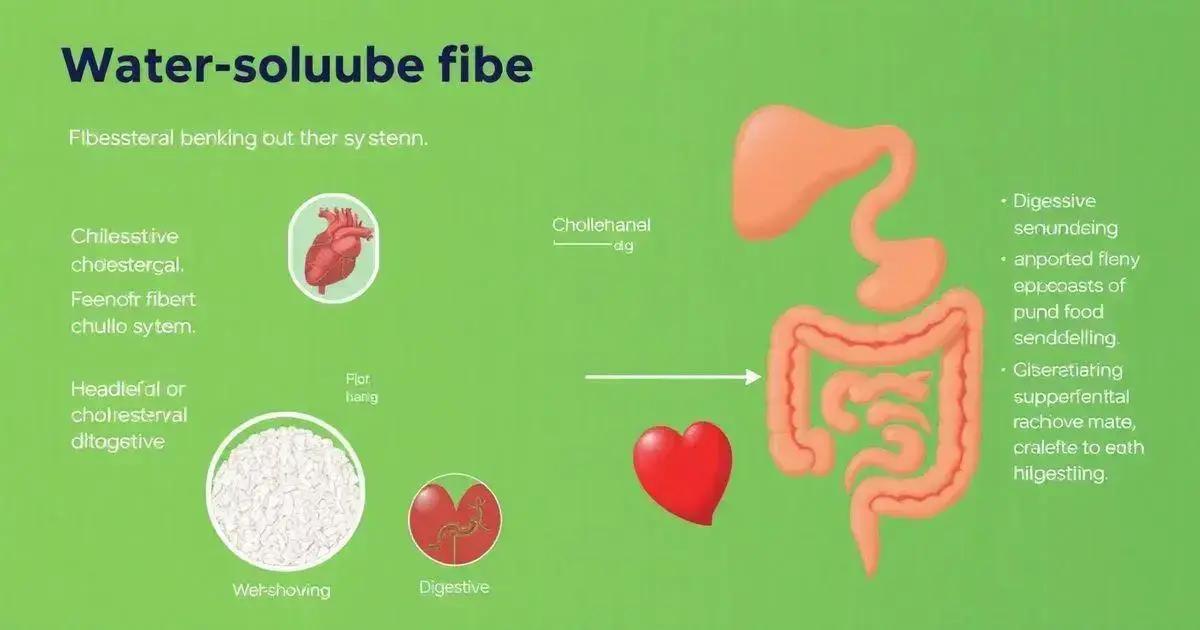
Fiber plays a crucial role in lowering cholesterol levels by utilizing several mechanisms in the body. When we consume water-soluble fiber, it dissolves in our digestive system and forms a gel-like substance. This gel binds with bile acids, which are made from cholesterol, and helps to excrete them.
How Does This Process Work?
In essence, when water-soluble fiber traps bile acids, the body has to use more cholesterol from the blood to produce new bile acids. This results in a decrease in the levels of LDL cholesterol, often referred to as ‘bad cholesterol’. The more soluble fiber we consume, the more cholesterol can be removed.
Additional Benefits of Fiber
Besides lowering LDL cholesterol, fiber also positively impacts overall heart health. Increased fiber intake can help regulate blood pressure and inflammation, two other significant factors that contribute to heart disease. Additionally, a diet rich in fiber can promote a healthier gut, which is essential for absorbing nutrients efficiently.
Research Supporting Fiber’s Role
Numerous studies support the claim that fiber can assist in cholesterol management. Research has shown that individuals who consume higher amounts of soluble fiber have lower cholesterol levels compared to those with a low-fiber diet. This makes understanding and incorporating fiber into daily eating habits vital for heart health.
By prioritizing foods high in water-soluble fiber, you can take proactive steps to maintain healthy cholesterol levels. This dietary choice not only supports cholesterol reduction but also promotes overall well-being.
Best Sources of Water-Soluble Fiber

Including water-soluble fiber in your diet is essential for lowering cholesterol and improving overall health. Here are some of the best sources of this type of fiber:
Oats
Oats are a fantastic source of water-soluble fiber. They contain beta-glucan, which is known for its cholesterol-lowering properties. Enjoy oatmeal for breakfast or add oats to smoothies for a nutritious boost.
Beans and Legumes
Beans, lentils, and peas are all rich in water-soluble fiber. Incorporate them into salads, soups, or stews. They not only help in reducing cholesterol but also provide protein and other essential nutrients.
Fruits
Certain fruits are excellent sources of water-soluble fiber. Apples, oranges, bananas, and berries are great choices. Enjoy them fresh, in smoothies, or as a healthy snack. The skins of some fruits also contribute beneficial fiber.
Vegetables
Vegetables like carrots, sweet potatoes, and Brussels sprouts are rich in water-soluble fiber. Including a variety of colorful vegetables in your meals can help you maximize your fiber intake.
Barley
Barley is another whole grain high in water-soluble fiber. It can be used in soups, stews, or as a side dish to enhance your fiber consumption.
By choosing these delicious and nutritious foods, you can easily increase your intake of water-soluble fiber, supporting your efforts to lower cholesterol levels and improve heart health.
Adding Fiber to Your Diet Effectively

Adding fiber effectively to your diet is essential for lowering cholesterol and improving overall health. Here are some practical tips to help you increase your water-soluble fiber intake:
1. Start Your Day with Fiber
Opt for a breakfast that includes high-fiber cereals or oatmeal. Adding fruits such as bananas or berries can enhance both flavor and fiber content.
2. Snack Smart
Choose fiber-rich snacks. Fresh fruits, raw vegetables, or nuts can serve as healthy snack options. For example, carrots or apple slices with nut butter are both nutritious and filling.
3. Incorporate Beans and Legumes
Add beans and legumes to your meals. They can be included in salads, soups, or casseroles. Lentils and chickpeas are versatile ingredients that boost fiber levels in any dish.
4. Read Food Labels
When shopping, look for food products high in fiber. Many packaged foods display fiber content on their labels. Aim for products that provide at least 3 grams of fiber per serving.
5. Gradually Increase Fiber Intake
When adding fiber to your diet, do it gradually to avoid digestive discomfort. This approach helps your body adjust to the increased fiber levels more comfortably.
6. Stay Hydrated
Drink plenty of water as you increase fiber intake. Fiber absorbs water, so staying hydrated is crucial for proper digestion and to prevent constipation.
By following these tips, you can effectively add water-soluble fiber to your daily diet, support healthy cholesterol levels, and improve your overall health.
The Importance of Water-Soluble Fiber in Your Diet
Incorporating water-soluble fiber into your diet is vital for reducing cholesterol levels and promoting heart health. This type of fiber not only aids in lowering LDL cholesterol but also improves overall digestive health and wellbeing.
By understanding the best sources of water-soluble fiber and how to effectively add it to your meals, you can take proactive steps toward better health. From oats and legumes to fruits and vegetables, numerous delicious options are available for everyone.
Making simple dietary changes can lead to significant health benefits, helping you lead a healthier lifestyle. Therefore, prioritize water-soluble fiber for a heart-healthy future.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Water-Soluble Fiber and Cholesterol
What is water-soluble fiber?
Water-soluble fiber is a type of dietary fiber that dissolves in water, forming a gel-like substance that helps to lower cholesterol levels.
How does water-soluble fiber help reduce cholesterol?
It binds with bile acids in the digestive system, leading to their excretion. The body then uses cholesterol from the blood to produce new bile acids, lowering LDL cholesterol levels.
What are some common sources of water-soluble fiber?
Common sources include oats, beans, fruits (like apples and oranges), and certain vegetables (like carrots and Brussels sprouts).
How can I add more fiber to my diet effectively?
Start with high-fiber breakfasts, snack on fruits and vegetables, and incorporate beans into meals. Gradually increase your fiber intake and stay hydrated.
What are the health benefits of increasing fiber intake?
Increasing fiber intake can help lower cholesterol, improve digestive health, regulate blood sugar levels, and promote a feeling of fullness.
Can I consume too much fiber?
While fiber is beneficial, consuming it in excessive amounts too quickly can lead to digestive discomfort. It’s important to increase fiber intake gradually.













