Vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to significant health issues, including fatigue, memory problems, and nerve damage. Treatment options include dietary changes, oral supplements, and injections, while long-term implications can impact overall well-being. Regular monitoring and addressing symptoms are crucial for effective management.
Vitamin B12 is essential for maintaining your overall health, yet many individuals may not recognize the signs of deficiency. Symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and memory issues can often be overlooked. In this article, we will explore how to recognize and treat vitamin B12 deficiency effectively, ensuring you understand the importance of this vital nutrient for your well-being. From understanding the key symptoms to exploring treatment options, let’s dive into how to safeguard your health.
Understanding Vitamin B12 Deficiency

Vitamin B12 deficiency is a condition that occurs when the body does not have enough vitamin B12 to function properly. This nutrient is crucial for producing red blood cells and maintaining a healthy nervous system.
Many people may be at risk of vitamin B12 deficiency without even realizing it. Vegetarians and vegans are particularly susceptible, as vitamin B12 is mainly found in animal products like meat, fish, and dairy. Additionally, older adults and individuals with certain medical conditions may have difficulty absorbing this important vitamin.
Causes of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
A deficiency can arise from several factors. One common reason is insufficient dietary intake. If your diet lacks adequate sources of vitamin B12, your body won’t get the required amount. Another cause can be malabsorption disorders, which affect the body’s ability to absorb nutrients from food.
Pernicious anemia, an autoimmune condition, can also prevent absorption of vitamin B12. The body cannot produce enough intrinsic factor, a protein needed to absorb B12 from the intestine. Other gastrointestinal issues, such as celiac disease and Crohn’s disease, may also contribute to this deficiency.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing a vitamin B12 deficiency. These include age, as older adults often have a decreased ability to absorb nutrients. Pregnant and breastfeeding women may also need additional B12 to support their health and the health of their babies.
The Importance of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 plays a vital role in DNA synthesis, neurological function, and the formation of red blood cells. Without adequate levels of this vitamin, a person may experience numerous health issues, highlighting the importance of understanding and addressing vitamin B12 deficiency.
Common Symptoms to Watch For
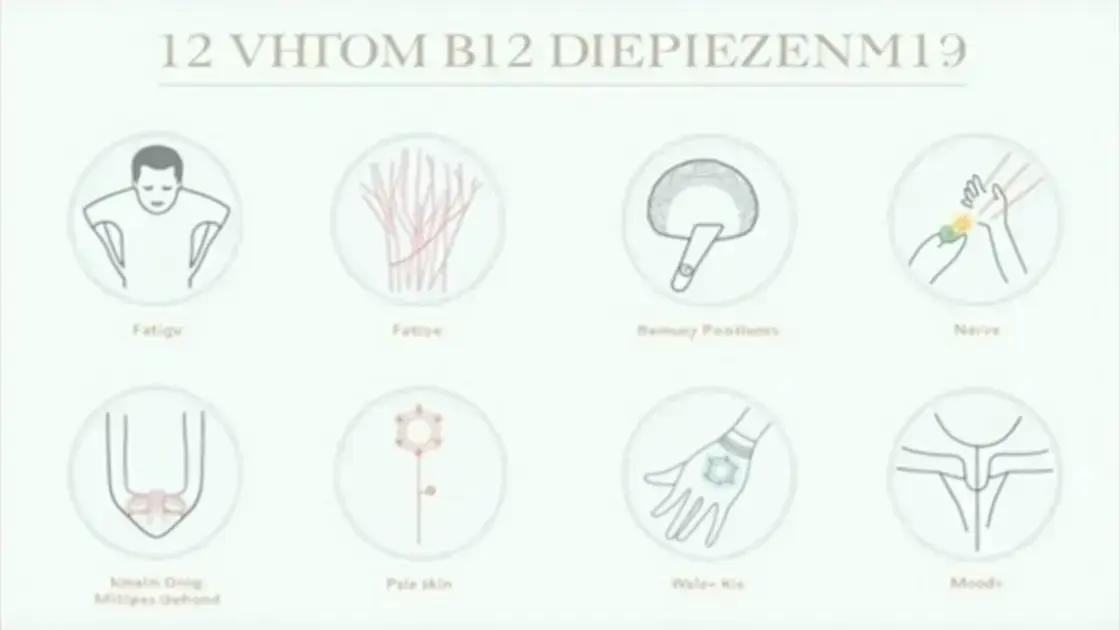
Recognizing the symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency is essential for maintaining your health. Many people experience subtle signs that can easily be overlooked. Here are some common symptoms to watch for:
Fatigue and Weakness
One of the earliest signs of a vitamin B12 deficiency is fatigue. You may feel unusually tired or weak even after a good night’s sleep. This happens because your body needs B12 to produce red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout your body.
Memory Problems
Vitamin B12 is vital for brain health. A deficiency can lead to memory issues or difficulties concentrating. You might find it challenging to remember names or follow conversations.
Nerve Problems
Another important symptom is nerve problems, which can manifest as tingling in the hands and feet. You may also experience difficulty walking or balance issues. These symptoms occur because vitamin B12 is essential for nerve function.
Pale or Jaundiced Skin
A lack of vitamin B12 can cause your skin to appear pale or even jaundiced, giving it a yellowish tint. This change happens because of a decrease in red blood cell production.
Mood Changes
A deficiency may also lead to mood changes, including feelings of depression or anxiety. Vitamin B12 plays a role in synthesizing brain chemicals that regulate mood.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional to evaluate your vitamin B12 levels and discuss potential treatments.
Effective Treatment Options
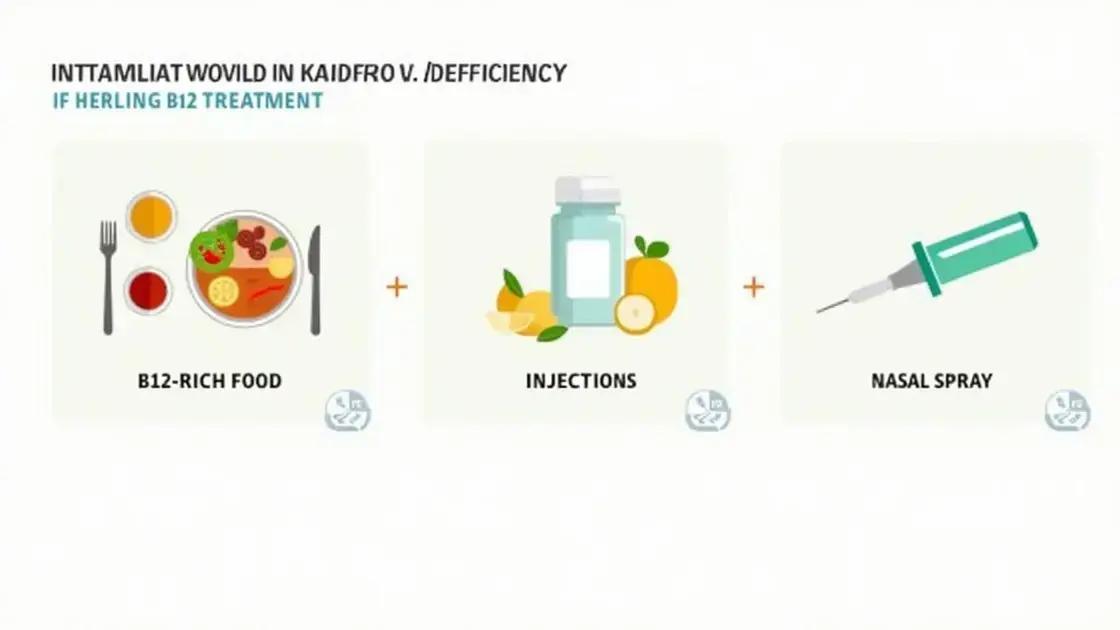
Treating a vitamin B12 deficiency effectively involves various options tailored to individual needs. Here are some common effective treatment methods:
Dietary Changes
One of the first steps is to improve your diet. Incorporate more vitamin B12-rich foods such as meat, fish, dairy products, eggs, and fortified cereals. For vegetarians or vegans, alternative sources may include fortified plant-based milks and nutritional yeast.
Oral Supplements
For many people, oral supplements can effectively restore vitamin B12 levels. These supplements are available in various strengths and forms, including tablets and sublingual versions. Always consult a healthcare provider to determine the right dosage for your needs.
Injections
In some cases, particularly for those with absorption issues, vitamin B12 injections may be necessary. These shots provide a quick and effective way to raise B12 levels in the body. Injections are usually given by a healthcare professional.
Nasal Sprays and Gel
Another option is nasal sprays or gels that deliver vitamin B12 directly into the bloodstream. These are helpful for individuals who prefer not to take oral supplements or have trouble with injections.
Regular Monitoring
It’s crucial to monitor your B12 levels regularly, especially if you are at risk for deficiency. Your doctor may recommend blood tests to ensure your levels remain adequate and to adjust treatment as needed.
By following these effective treatment options, you can manage vitamin B12 deficiency successfully and improve your overall health.
Long-term Health Implications
Long-term vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to serious health issues that impact various body systems. It’s important to recognize these potential implications to manage your health effectively.
Nervous System Damage
One of the most concerning issues is permanent nerve damage. Vitamin B12 is crucial for maintaining the health of nerve cells. Prolonged deficiency may lead to numbness or tingling in the extremities and difficulties with movement.
Memory Loss and Cognitive Decline
Long-term deficiency may also increase the risk of memory loss and cognitive decline. Studies suggest that inadequate B12 levels can contribute to conditions like dementia or other neurocognitive disorders in older adults.
Heart Health Risks
Chronic vitamin B12 deficiency can affect heart health as well. It leads to an increase in homocysteine, an amino acid associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases. Managing B12 levels may help in reducing these risks.
Anemia
Another long-term implication is the risk of developing pernicious anemia. This condition results in the body producing fewer red blood cells, which can cause severe fatigue, weakness, and other health problems.
Impact on Overall Well-Being
Overall, the long-term implications of untreated vitamin B12 deficiency can drastically affect one’s quality of life. It’s essential to monitor and address any deficiency to ensure a healthy, active lifestyle.
In Summary: Recognizing and Treating Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency is a critical health concern that can lead to serious long-term implications, including nerve damage, memory loss, and cardiovascular risks. By understanding the symptoms, effective treatment options, and the potential health impacts, you can take proactive steps to manage your vitamin B12 levels.
Ensuring a diet rich in vitamin B12, utilizing supplements when necessary, and consulting with healthcare professionals are important strategies to maintain optimal health.
With proper recognition and treatment, you can protect your overall wellbeing and enhance your quality of life.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions About Vitamin B12 Deficiency
What is vitamin B12 deficiency?
Vitamin B12 deficiency occurs when the body does not have enough vitamin B12, which is essential for producing red blood cells and maintaining a healthy nervous system.
What are the common symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency?
Common symptoms include fatigue, weakness, memory problems, nerve issues like tingling, pale or jaundiced skin, and mood changes.
How can I treat vitamin B12 deficiency?
Treatment options include dietary changes to include more B12-rich foods, oral supplements, injections, and nasal sprays, depending on individual needs.
What are the long-term health implications of untreated vitamin B12 deficiency?
Long-term implications can include nerve damage, cognitive decline, increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, and anemia.
Who is at risk for vitamin B12 deficiency?
Individuals at risk include vegetarians, vegans, older adults, and those with absorption disorders or certain medical conditions.
How can I monitor my vitamin B12 levels?
Consult your healthcare provider for regular blood tests to monitor your vitamin B12 levels, especially if you are at risk for deficiency.













