To prevent overexertion during physical activities, understand its signs, such as fatigue and dizziness, stay hydrated, set realistic goals, take regular breaks, and know when to seek medical advice for persistent symptoms.
Overexertion during physical activities can lead to serious injuries and setbacks in your fitness journey. Understanding how to prevent overexertion is crucial for everyone, whether you’re a seasoned athlete or just starting. In this post, we will delve into the key signs of overexertion, practical tips to keep your workouts safe, and when to seek professional advice. With these insights, you can enjoy a healthier, more effective fitness routine without the risk of pushing your body too far.
Understanding Overexertion
Understanding Overexertion is essential for anyone engaging in physical activities. It occurs when you push your body beyond its physical limits. Knowing your limits is key to maintaining a healthy workout routine.
Overexertion can affect anyone, regardless of fitness level. It may happen during exercise, sports, or daily activities. It can lead to fatigue, injuries, and long-term health issues if not managed properly.
Causes of Overexertion
Several factors can contribute to overexertion, including:
- Inadequate rest: Not allowing your body sufficient recovery time can lead to overexertion.
- Improper technique: Engaging in exercises without proper form increases the risk of injury.
- Overtraining: Working out too frequently without enough recovery time can exhaust muscles.
- Environmental factors: Extreme heat or cold can increase the risk of overexertion.
Importance of Awareness
Being aware of overexertion is vital. This awareness helps you listen to your body, ensuring you take breaks when necessary.
Monitoring your physical activity can prevent injuries and promote a balanced workout routine. Always aim for a gradual increase in intensity. This will allow your body to adjust safely to new levels of exertion.
Signs of Overexertion to Watch For
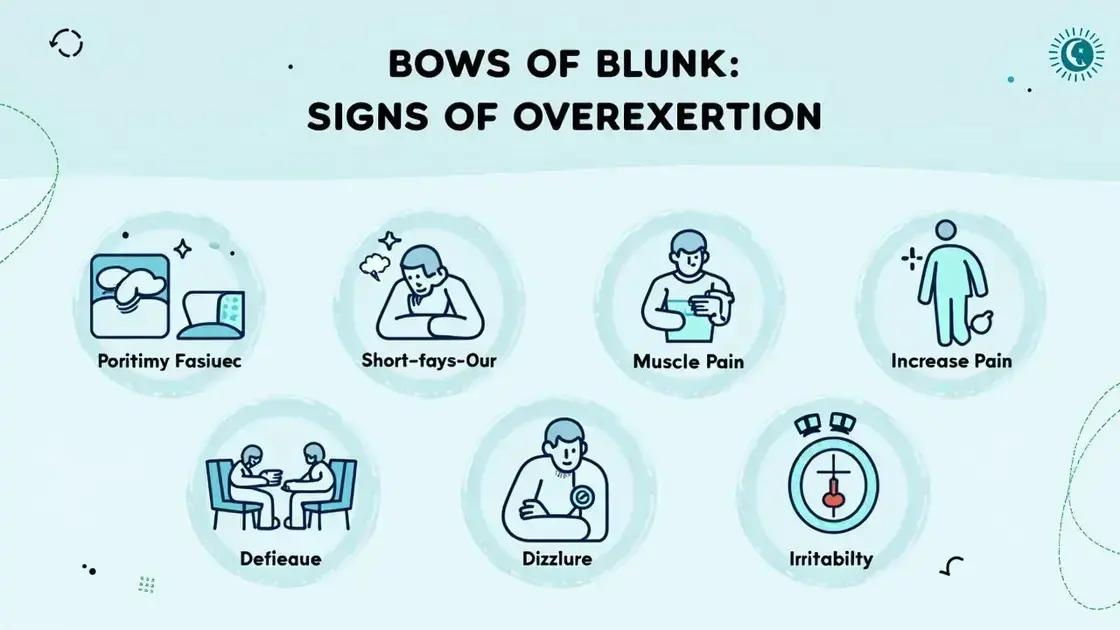
Signs of Overexertion to Watch For include several clear indicators that may signal your body is working too hard. Recognizing these signs early is crucial for preventing future issues.
1. Fatigue: A notable increase in tiredness during or after physical activities can indicate overexertion. If you find yourself unusually drained, it may be time to slow down.
2. Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or feeling winded more than usual is a significant sign that you may be overexerting yourself. Pay attention to your breathing rhythm.
3. Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Feeling dizzy, lightheaded, or faint during exercise is a serious warning sign. Stop your activity and take a break if this occurs.
4. Muscle Pain: While some soreness is normal after exercising, sharp or persistent pain may indicate that you’re pushing too hard. It’s important to differentiate between typical muscle fatigue and pain.
5. Increased Heart Rate: An elevated heart rate that doesn’t decrease with rest could signal that you are overexerting yourself. Monitoring your heart rate can be helpful in detecting this.
6. Irritability: Mental signs like irritability, mood swings, or lack of motivation can signal overexertion. Physical exertion affects our mental state, so take note of your mood during workouts.
Keeping Track of Your Body
Being aware of these signs can help you adjust your workouts to maintain a healthy balance. It’s essential to listen to your body during any physical activity.
Tips to Prevent Overexertion

Tips to Prevent Overexertion are essential for anyone who wants to stay active while ensuring their safety and well-being. Here are some helpful strategies to keep in mind:
1. Warm Up and Cool Down
Before every workout, spend at least 5 to 10 minutes warming up. Gentle exercises prepare your muscles and heart for physical activity. Similarly, cooling down helps your body recover.
2. Stay Hydrated
Drinking water before, during, and after exercise can prevent dehydration. Keep a water bottle handy to remember to stay hydrated throughout your activities.
3. Listen to Your Body
Always pay attention to how your body feels. If you experience signs of fatigue or discomfort, it’s vital to take a break or scale back your activity level. Your body knows best!
4. Set Realistic Goals
Start with achievable fitness goals and gradually increase your activity level. Setting unrealistic expectations can lead to pushing yourself too hard.
5. Take Regular Breaks
Incorporate breaks into your physical activities, especially during longer sessions. Resting helps recharge your body and lowers the risk of overexertion.
6. Cross-Train
Engage in a variety of exercises to work different muscle groups. This helps reduce the risk of injury and keeps your workouts fresh and enjoyable.
7. Seek Professional Guidance
If you’re unsure about your workout routine, consider consulting a trainer or coach. They can provide personalized advice to help you avoid overexertion.
When to Seek Medical Advice
When to Seek Medical Advice is a crucial aspect of preventing overexertion during physical activities. Knowing when to consult a healthcare professional can help ensure your health and safety.
1. Persistent Pain: If you experience muscle or joint pain that lasts more than a few days or worsens over time, it is important to seek medical help. Chronic pain can indicate an underlying injury.
2. Difficulty Breathing: If you find it hard to breathe normally during or after exercise, you should seek medical advice immediately. This could be a sign of a serious condition.
3. Dizziness or Fainting: Feeling dizzy, lightheaded, or faint during physical activity is a red flag. If this happens frequently, consult a doctor to rule out any health issues.
4. Heart Palpitations: An unusually fast or irregular heartbeat could signal overexertion. If these symptoms occur often, it’s essential to see a healthcare professional.
5. Changes in Vision: Sudden changes in your eyesight, such as blurred vision or seeing spots, need prompt medical evaluation, especially during physical activities.
6. Severe Headaches: If you experience headaches that become severe or different from your usual headaches after exercise, contact your doctor for further evaluation.
7. Unusual Fatigue: If you feel excessively tired even after a restful period, this could indicate a more serious health concern. Getting professional advice is wise in this situation.
In Summary: Preventing Overexertion is Key
Preventing overexertion during physical activities is essential for maintaining a healthy lifestyle and avoiding injuries. By understanding overexertion and recognizing its signs, you can take proactive measures to safeguard your well-being.
Implementing tips such as warming up, staying hydrated, and listening to your body can go a long way in ensuring a safe exercise experience. Additionally, knowing when to seek medical advice is crucial in addressing potential health concerns early on.
By being aware of these factors and practicing smart physical activity habits, you can enjoy your workouts while maintaining your health and safety.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions About Preventing Overexertion
What is overexertion?
Overexertion occurs when you push your body beyond its physical limits, leading to fatigue, pain, and potential injury.
What are the signs of overexertion?
Signs of overexertion include fatigue, dizziness, difficulty breathing, persistent pain, and increased heart rate.
How can I prevent overexertion during exercise?
You can prevent overexertion by warming up, staying hydrated, setting realistic goals, and listening to your body during activities.
When should I seek medical advice?
You should seek medical advice if you experience persistent pain, difficulty breathing, dizziness, severe headaches, or unusual fatigue.
Is it normal to feel sore after exercising?
Some soreness is normal after exercising, especially if you are trying new activities. However, sharp or persistent pain should be evaluated.
Can I continue exercising if I feel tired?
It’s important to listen to your body. If you’re feeling tired, taking a break or resting is recommended to prevent overexertion.












