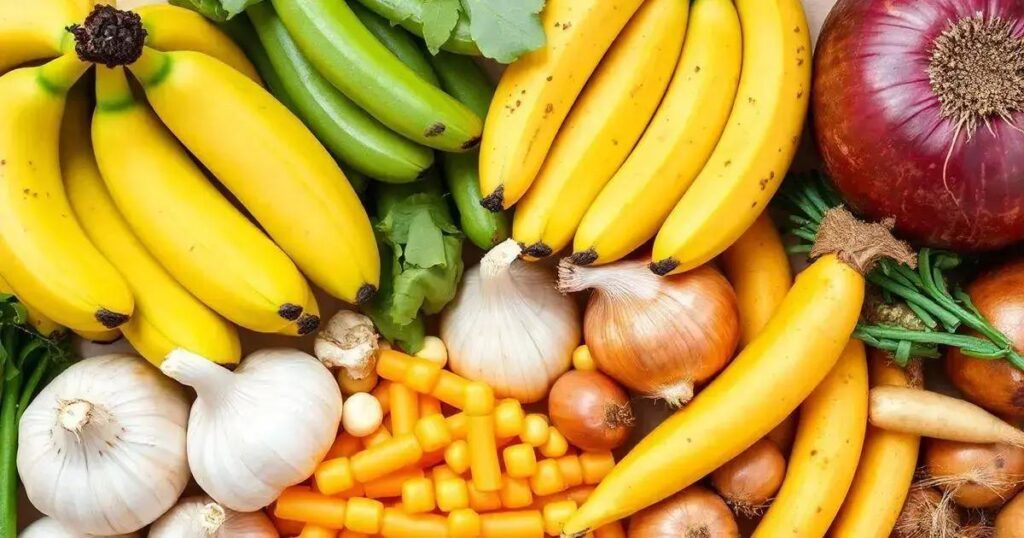
To prevent digestive issues, incorporating prebiotic foods such as garlic, onions, asparagus, and bananas into your diet is essential. These foods nourish beneficial gut bacteria, promoting a balanced microbiome and enhancing digestion. Start slowly, mix prebiotics into meals, and listen to your body’s response for optimal gut health.
Digestive issues can disrupt our daily lives, causing discomfort and frustration. Many people suffer from these problems, but did you know that incorporating prebiotic foods into your diet can help prevent them? Prebiotic foods are essential for nurturing beneficial gut bacteria and promoting overall digestive health. In this article, we will explore how to prevent digestive issues with prebiotic foods, discussing their benefits, various types, and practical tips for including them in your meals.
Understanding Digestive Issues
Understanding Digestive Issues is crucial for maintaining a healthy life. Many people experience problems like bloating, gas, constipation, and diarrhea, which can significantly affect their daily activities.
Digestive issues can arise from various factors, including poor diet, stress, and lack of physical activity. For instance, eating too many processed foods can lead to an imbalance of good and bad bacteria in the gut.
Another common cause is food intolerances. Some individuals may find certain foods hard to digest, leading to discomfort and gastrointestinal distress. Identifying these triggers can help manage symptoms effectively.
Symptoms of digestive issues can manifest in different ways. For example, bloating can occur when your stomach fills with air or gas, often making you feel uncomfortable. Gas usually results from the breakdown of food in the intestines, which can be exacerbated by eating certain types of foods.
Additionally, constipation happens when bowel movements are difficult or infrequent, while diarrhea results in loose or watery stools. Both conditions highlight the body’s struggle to process food effectively.
Lastly, gut health plays a vital role in overall health. A balanced gut microbiome helps in the absorption of nutrients, supports the immune system, and influences your mood. The more we understand these digestive issues, the better equipped we are to prevent them.
The Role of Prebiotic Foods

The Role of Prebiotic Foods is essential in maintaining a healthy digestive system. Prebiotic foods are types of dietary fiber that feed the good bacteria in your gut. By consuming these foods, you can help create a balanced gut microbiome, which is crucial for digestion.
These foods act as fuel for beneficial gut bacteria. When you eat prebiotic-rich foods, the fiber passes through your digestive system undigested. In the intestines, good bacteria ferment this fiber and produce short-chain fatty acids that support gut health.
Research suggests that a healthy gut can improve digestion, enhance immune function, and even affect your mood. Prebiotic foods can help prevent dysbiosis, which is an imbalance of gut bacteria that can lead to digestive issues.
Additionally, prebiotic foods can aid in the absorption of essential minerals like calcium and magnesium. This means a proper intake of prebiotics may also contribute to stronger bones and overall better health.
Some examples of prebiotic foods include garlic, onions, leeks, asparagus, and bananas. Incorporating these foods into your meals can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria, helping to enhance your digestive health.
Furthermore, prebiotic foods may help reduce the risk of certain chronic diseases by improving overall gut health. When gut bacteria are flourishing, they produce compounds that may lower inflammation and improve metabolic health.
Top Prebiotic Foods to Include

Incorporating top prebiotic foods into your diet can greatly benefit your digestive health. Here are some of the most effective and tasty prebiotic foods you should include:
- Garlic: Garlic is not only a delicious addition to many dishes, but it also contains a type of fiber called inulin, which helps nourish the good bacteria in the gut.
- Onions: Onions are rich in inulin and another prebiotic fiber called fructooligosaccharides (FOS). They can easily be added to soups, salads, and various recipes.
- Leeks: Similar to garlic and onions, leeks also provide inulin. Incorporating leeks into your meals can enhance the flavor while supporting gut health.
- Asparagus: Asparagus is not just a nutritious vegetable; it is high in prebiotic fiber as well. Grilled or roasted asparagus can be a tasty side dish.
- Bananas: Bananas are an excellent source of resistant starch, which has prebiotic effects. They make for a perfect snack or addition to smoothies.
- Apples: Apples contain pectin, a fiber that acts as a prebiotic. Eating apples can help improve your digestive health.
- Oats: Oats provide beta-glucan, a soluble fiber that can promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
- Chicory Root: Chicory root is one of the richest sources of inulin and can be consumed as a supplement or added to foods.
- Artichokes: Artichokes are another great source of inulin. They can be boiled, roasted, or used in dips.
- Berries: Berries like blueberries and strawberries also contribute prebiotic benefits while offering delicious taste and antioxidants.
Including a variety of these foods in your meals not only enhances flavor but also supports a healthy gut.
Tips for Incorporating Prebiotics into Your Diet

Incorporating prebiotics into your diet can be simple and enjoyable. Here are some tips to help you get started:
- Start Slowly: If you are new to prebiotics, begin with small amounts. Gradually increase intake to help your digestive system adjust without discomfort.
- Mix into Meals: Add prebiotic foods like sliced bananas or chopped garlic into your breakfast cereal or smoothies for a yummy boost.
- Use in Cooking: Incorporate onion and leek in soups or stir-fries. Their flavors enhance dishes while providing essential prebiotics.
- Snacks Matter: Choose snacks that contain prebiotic fibers, such as apple slices with nut butter or yogurt topped with berries.
- Make Salads Exciting: Include raw vegetables like onions and asparagus in your salads. They can add crunch and promote gut health.
- Try Fermented Foods: Combine prebiotic foods with fermented options like yogurt or kimchi to create a balanced gut-friendly diet.
- Plan Your Meals: Prepare a weekly meal plan that includes prebiotic foods. Having these ingredients on hand can make it easier to include them in your diet.
- Explore New Recipes: Look for recipes that star prebiotic foods. Cooking with these ingredients can be fun and flavorful.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water when increasing fiber intake. Hydration can help prevent any digestive discomfort.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how your body reacts as you incorporate more prebiotics. Adjust your intake based on your comfort level.
By making these small adjustments to your diet, you can enjoy the many benefits of prebiotics while supporting your digestive health.
Embracing Prebiotic Foods for Digestive Health
Incorporating prebiotic foods into your diet is a simple and effective way to improve your digestive health. Understanding the role of prebiotics, recognizing the top foods to include, and applying practical tips can lead to a happier gut.
By making small changes to your meals and exploring various recipes, you can easily nourish the beneficial bacteria in your gut, reduce digestive issues, and promote overall well-being. Remember, listening to your body and adjusting your intake of prebiotics can further enhance your digestive experience.
As you explore the world of prebiotic foods, you will discover the delicious flavors and health benefits they bring to your plate.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Prebiotic Foods
What are prebiotic foods and why are they important?
Prebiotic foods are types of dietary fiber that feed good bacteria in your gut, helping to promote gut health and improve digestion.
How can I incorporate prebiotic foods into my diet?
You can incorporate prebiotic foods by adding items like garlic, onions, leeks, and bananas into your meals and snacks.
What are some examples of common prebiotic foods?
Common prebiotic foods include garlic, onions, asparagus, bananas, oats, chicory root, and artichokes.
Are there any side effects from consuming prebiotics?
While prebiotics are generally safe, some people may experience digestive discomfort if they increase fiber intake too quickly. It’s best to start slow.
How do prebiotic foods differ from probiotics?
Prebiotics are fibers that feed and support beneficial gut bacteria, while probiotics are live bacteria that contribute to gut health.
Can prebiotic foods help with weight management?
Yes, prebiotic foods can help with weight management by promoting a healthy gut microbiome, which plays a role in metabolism and appetite regulation.













