To address muscle cramps effectively, incorporate magnesium-rich foods like leafy greens, nuts, and whole grains into your diet, stay hydrated, warm up before exercise, and maintain balanced electrolytes to support muscle function and prevent discomfort.
Muscle cramps can be a painful experience for many people, often caused by dehydration, overexertion, or nutrient deficiencies. In particular, magnesium plays a crucial role in muscle function and may help alleviate cramps. This article will explore how to address muscle cramps with magnesium-rich foods, providing insights on effective dietary choices and tips for maintaining healthy muscle function.
Understanding Muscle Cramps and Their Causes

Muscle cramps are sudden, involuntary contractions of one or more muscles. They can occur in various parts of the body, especially in the legs, and are often sharp and painful. The exact cause of muscle cramps can vary, but some common factors contribute to their occurrence.
Dehydration
One significant cause of muscle cramps is dehydration. When the body loses too much fluid, it can lead to imbalances in electrolyte levels, triggering cramps. Staying hydrated, especially during physical activity, is important.
Overexertion and Strain
Overexerting muscles during exercise, especially if you are not used to physical activity, can lead to cramps. Intense activity can cause muscles to fatigue and contract as they are pushed beyond their limits.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Lack of important nutrients, particularly minerals like magnesium, potassium, and calcium, can cause muscle cramps. These nutrients help regulate muscle contractions and maintain proper function.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can also cause muscle cramps. Conditions such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, and nerve compression can make cramps more frequent. If cramps persist, consulting a healthcare professional is recommended.
The Role of Magnesium in Muscle Function
Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a vital role in muscle function. It helps with the contraction and relaxation of muscles. This mineral affects muscles on a cellular level, influencing how they respond during physical activity.
Muscle Contraction
When a muscle is stimulated to contract, magnesium works alongside calcium. Calcium enters muscle cells to trigger contraction, while magnesium helps the muscle relax afterward. A balance of these two minerals is crucial to prevent prolonged contractions, or cramps.
Energy Production
Magnesium also aids in energy production. It plays a vital role in converting food into energy that muscles can use during exercise. Without sufficient magnesium, the body may struggle to produce energy, leading to fatigue and weakness.
Preventing Muscle Cramps
By ensuring enough magnesium in the diet, individuals can help prevent muscle cramps. This is especially important for athletes or those engaging in strenuous activities. Adequate magnesium levels can reduce the risk of cramping and improve overall performance.
Sources of Magnesium
Magnesium can be found in many foods, such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. Including these magnesium-rich foods in your diet is an excellent way to support muscle function and overall health.
Top Magnesium-Rich Foods to Include in Your Diet
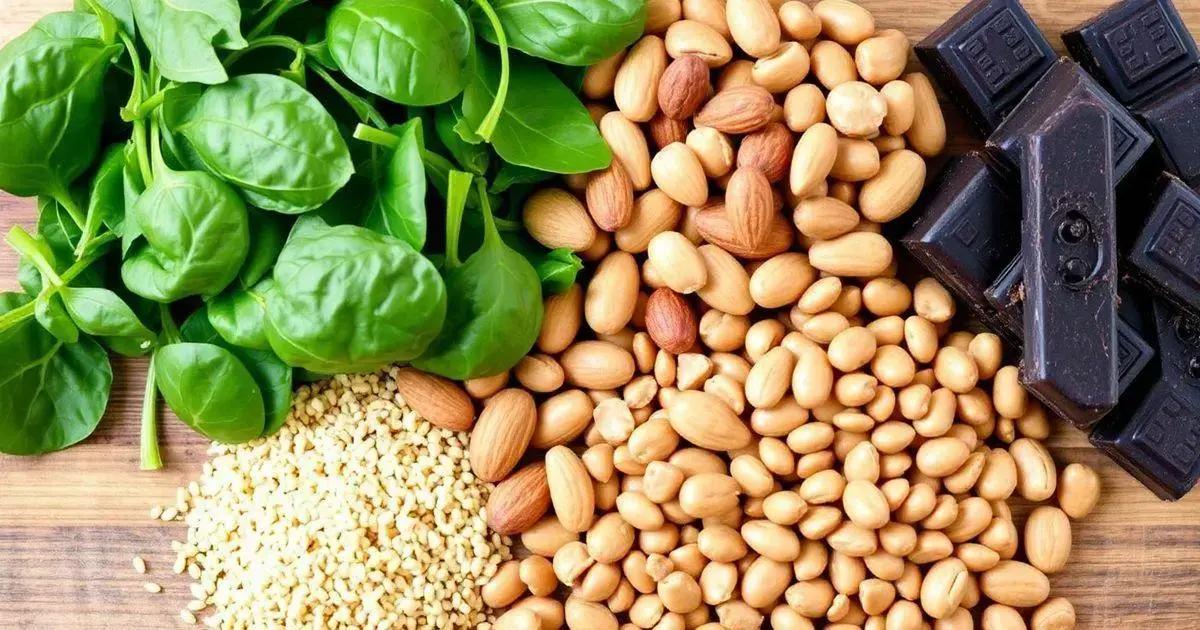

Including magnesium-rich foods in your diet is essential for preventing muscle cramps and maintaining good health. Here are some top sources of magnesium:
Leafy Greens
Spinach and kale are excellent sources of magnesium. These versatile greens can be added to salads, smoothies, or cooked dishes.
Nuts and Seeds
Almonds, cashews, and pumpkin seeds are not only high in magnesium but also offer healthy fats. Snack on them or add them to yogurt and oatmeal for an extra boost.
Whole Grains
Foods like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread provide magnesium and are great sources of fiber. Swap out white grains for whole grains in your meals.
Legumes
Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are rich in magnesium and protein. Incorporating these into soups, salads, and dips can enhance nutrient intake.
Dark Chocolate
Good news for chocolate lovers! Dark chocolate (containing at least 70% cocoa) is high in magnesium. Enjoy it in moderation for a tasty treat.
Fish
Certain fish, like salmon and mackerel, are great magnesium sources and provide healthy omega-3 fatty acids. Include these in your meals for both magnesium and heart health.
Tips for Preventing Muscle Cramps
Preventing muscle cramps is essential for anyone who wants to maintain an active lifestyle. Here are some useful tips to help you avoid cramps:
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water throughout the day is crucial. Dehydration can lead to muscle cramps, so make sure to replenish fluids before, during, and after exercises.
Warm-Up and Stretch
Before physical activity, always warm up your muscles with light exercises and stretches. This helps prepare your muscles for more intense movements, reducing the risk of cramps.
Incorporate Magnesium-Rich Foods
Including magnesium-rich foods in your diet can support muscle function. Foods like spinach, nuts, and whole grains help prevent cramps by maintaining proper muscle function.
Maintain Balanced Electrolytes
Ensure you consume a balanced amount of electrolytes, including sodium, potassium, and calcium, along with magnesium. This balance helps muscles function properly and can reduce cramping.
Listen to Your Body
If you start to feel pain or discomfort during physical activity, take a break. Pushing through the pain can lead to cramps and even injury, so it’s important to listen to your body.
Regular Exercise
Staying physically active helps strengthen your muscles and can reduce the frequency of cramps. Regular exercise improves your overall muscle condition and tolerance.
In Summary: Addressing Muscle Cramps with Magnesium-Rich Foods
Muscle cramps can be a frustrating and painful experience, but understanding their causes and how to address them is crucial. By recognizing the important role magnesium plays in muscle function, you can take proactive steps to prevent cramps.
Incorporating magnesium-rich foods like leafy greens, nuts, and whole grains into your diet, along with staying hydrated and maintaining electrolyte balance, can make a significant difference.
Additionally, embracing proper warm-up routines and listening to your body during physical activities can help you avoid cramps for a more enjoyable and active lifestyle.
Implementing these strategies will not only reduce the frequency of muscle cramps but also enhance your overall health and performance.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Addressing Muscle Cramps
What are muscle cramps?
Muscle cramps are sudden, involuntary contractions of one or more muscles, usually causing sharp pain and discomfort.
How does magnesium help prevent muscle cramps?
Magnesium plays a crucial role in muscle contraction and relaxation, helping to maintain proper muscle function and reduce the risk of cramps.
What are some magnesium-rich foods?
Foods rich in magnesium include leafy greens like spinach, nuts such as almonds, whole grains like quinoa, and legumes.
How can I stay hydrated to prevent muscle cramps?
Drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially before, during, and after exercise to maintain hydration and prevent cramps.
What are some effective tips for preventing muscle cramps?
To prevent muscle cramps, warm up and stretch before exercising, stay hydrated, consume a balanced diet with electrolytes, and listen to your body during activity.
Can regular exercise help reduce muscle cramps?
Yes, regular exercise strengthens muscles and improves overall fitness, which can help reduce the frequency of muscle cramps.













