The importance of avoiding overuse of painkillers lies in understanding their types, associated risks like dependence and gastrointestinal issues, responsible usage guidelines, and exploring effective alternatives such as physical therapy, exercise, and mind-body techniques for pain management.
Painkillers are widely used to alleviate discomfort, but the importance of avoiding overuse of painkillers cannot be understated. Over-reliance on these medications can lead to serious health risks, including dependency and other complications. This article will discuss the different types of painkillers, the associated risks of overuse, how to use them responsibly, and explore alternative options for effective pain management.
Understanding Painkillers and Their Uses

Painkillers, also known as analgesics, are medications used to relieve pain. Different types of painkillers serve varied purposes to help manage discomfort. Understanding these medications is essential for safe and effective pain relief.
Types of Painkillers
There are mainly three categories of painkillers:
- Over-the-Counter (OTC) Painkillers: These are available without a prescription. Common examples are acetaminophen (Tylenol) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve).
- Prescription Painkillers: More potent medications, prescribed by a doctor, include opioids such as morphine, oxycodone, and hydrocodone. These are meant for severe pain.
- Adjuvant Medications: These are not primarily painkillers but are used to enhance pain relief. Antidepressants and anticonvulsants can help manage chronic pain conditions.
How Painkillers Work
Painkillers work by blocking pain signals from reaching the brain or by interfering with the brain’s perception of pain. This mechanism allows individuals to feel more comfortable during recovery or when dealing with chronic pain.
Proper Use of Painkillers
Understanding the correct use of painkillers is vital. Always follow the dosing instructions provided by a healthcare professional or on the medicine label. Misusing painkillers can lead to serious health issues, including addiction.
When taking painkillers, be aware of potential side effects such as drowsiness, stomach upset, or, in the case of opioids, the risk of overdose. It’s crucial to consult with a doctor if pain persists or worsens.
Risks Associated with Overusing Painkillers
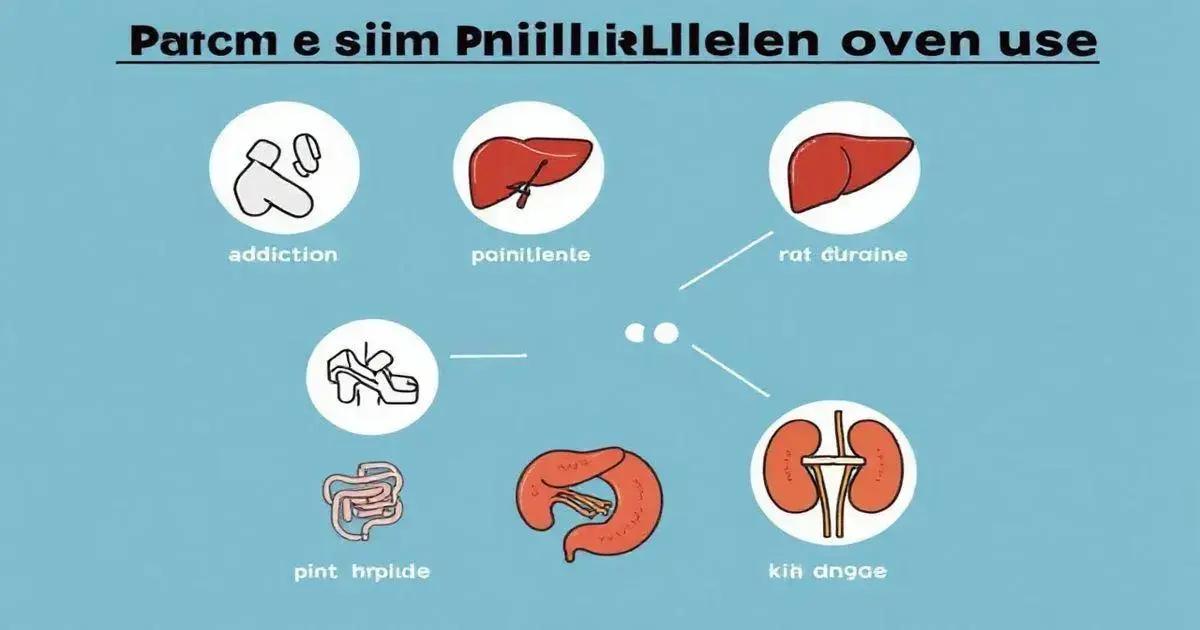
Overusing painkillers can lead to several serious health risks. While these medications are effective in treating pain, improper usage can cause harmful side effects.
Dependence and Addiction
One of the most significant risks associated with overusing painkillers, especially opioids, is the potential for dependence. The body may become accustomed to the presence of the medication, leading to a situation where more pills are needed to achieve the same effect. This can result in addiction, where individuals may find themselves unable to stop using the drug despite harm to their health.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Regularly taking painkillers, particularly NSAIDs, can cause gastrointestinal problems. These medications can irritate the stomach lining, leading to conditions such as ulcers or gastrointestinal bleeding. Patients may experience symptoms like nausea, vomiting, or persistent stomach pain.
Liver Damage
Acetaminophen, a common over-the-counter painkiller, can lead to liver damage when taken in high doses or combined with alcohol. The liver metabolizes acetaminophen, and excessive intake can overwhelm this organ and result in serious health problems.
Kidney Damage
Overuse of certain painkillers can also affect kidney function. NSAIDs, in particular, can decrease blood flow to the kidneys, causing damage over time. This may lead to kidney disease, which might require medical intervention or dialysis.
Long-term use of pain medications should always be discussed with a healthcare provider to minimize risks and ensure safe pain management. Understanding the associated risks of overusing painkillers ensures better health choices and long-term wellbeing.
How to Use Painkillers Responsibly

Using painkillers responsibly is crucial for ensuring your health and safety. Here are some important guidelines to follow.
Follow Dosage Instructions
Always adhere to the dosage instructions provided by your healthcare provider or listed on the medication packaging. Taking more than the recommended amount can increase the risk of serious side effects or overdose.
Limit Duration of Use
Avoid using painkillers for extended periods. If you find yourself needing them regularly, consult with a healthcare professional. They can help you explore other treatment options and determine the best course of action.
Communicate with Your Doctor
Discuss any current medications or health conditions with your doctor. They can provide guidance on which painkillers are safe for you to use, especially if you have underlying health issues or are taking other medications.
Be Aware of Side Effects
Understand the potential side effects of the painkiller you are taking. Common side effects may include dizziness, nausea, or drowsiness. If you experience severe side effects, seek medical attention immediately.
Avoid Mixing Medications
Do not mix painkillers with other medications or alcohol without first consulting your doctor. Certain combinations can lead to dangerous interactions and increase the risk of harmful effects.
Keep Medication Secure
Store painkillers in a secure location, out of reach of children and anyone who might misuse them. Proper storage can help prevent accidental ingestion or abuse.
By following these guidelines, you can use painkillers effectively while minimizing the risks associated with their use.
Alternatives to Painkillers for Pain Management

Exploring alternatives to painkillers for pain management can provide relief without the risks associated with these medications. Here are some effective options:
Physical Therapy
Working with a physical therapist can help strengthen muscles and improve flexibility. This approach can reduce pain and enhance mobility, proving beneficial for chronic pain conditions.
Exercise
Regular physical activity can release endorphins, which are natural pain relievers. Low-impact exercises, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can help manage pain effectively.
Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat pads or cold packs can alleviate pain. Heat therapy can help relax tense muscles, while cold therapy can reduce inflammation and numb acute pain.
Acupuncture
This traditional Chinese medicine technique involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to relieve pain. Many people find acupuncture helpful for managing various types of pain.
Mind-Body Techniques
Practices like yoga, meditation, and guided imagery can help manage pain. These techniques promote relaxation and can alter the body’s perception of pain.
Herbal Remedies
Certain herbs, such as turmeric and ginger, possess anti-inflammatory properties. These natural remedies can be incorporated into your diet or taken in supplement form to help reduce pain.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
This psychological approach can help change negative thought patterns related to pain. CBT teaches coping strategies and can provide individuals with tools to manage their pain effectively.
Each alternative may work differently for each person, so it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to find the most suitable options for your specific situation.
In Summary: Responsible Pain Management
Understanding the importance of avoiding overuse of painkillers is crucial for maintaining long-term health. By being aware of the different types of painkillers, their associated risks, and how to use them responsibly, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their pain relief options.
Additionally, exploring alternatives such as physical therapy, exercise, and mind-body techniques can offer effective pain management solutions without the unwanted side effects of medications. Prioritizing a balanced approach to pain management not only enhances overall well-being but also reduces the likelihood of dependence and health complications.
Consulting with healthcare professionals is essential for developing a personalized pain management plan that considers all available options for relief.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Painkillers and Pain Management
What are the different types of painkillers?
Painkillers can be classified into three main categories: over-the-counter (OTC) medications, prescription medications, and adjuvant medications that enhance pain relief.
What are the risks associated with overusing painkillers?
Overusing painkillers can lead to dependence, addiction, gastrointestinal issues, liver damage, and kidney damage.
How can I use painkillers responsibly?
Follow dosage instructions, limit the duration of use, communicate with your doctor, be aware of side effects, avoid mixing medications, and keep medication secure.
What are some alternatives to painkillers for managing pain?
Alternatives include physical therapy, regular exercise, heat and cold therapy, acupuncture, mind-body techniques like yoga and meditation, herbal remedies, and cognitive behavioral therapy.
When should I consult a healthcare professional about my pain?
Consult a healthcare professional if you experience persistent pain, find yourself regularly needing painkillers, or experience severe side effects.
Can lifestyle changes help in pain management?
Yes, making lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, staying active, and managing stress can significantly improve pain management.













