The benefits of daily fiber for digestive health include promoting regular bowel movements, preventing constipation, supporting a healthy gut microbiome, and reducing the risk of digestive disorders. Incorporating fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes into your diet can significantly enhance overall well-being.
Daily fiber plays a crucial role in maintaining digestive health. By eating a variety of fiber-rich foods, you can enhance gut health, prevent constipation, and promote regular bowel movements. In this blog post, we will delve into the essential benefits of daily fiber for digestive health, explore outstanding sources of fiber, and provide practical tips for incorporating it into your diet.
Understanding Daily Fiber and Its Importance

Daily fiber is a type of carbohydrate that cannot be digested by the human body. It is essential for our overall health, particularly for maintaining good digestive health. The importance of daily fiber lies in its ability to aid digestion, prevent constipation, and support a healthy gut microbiome.
Why is Fiber Important?
Fiber plays a key role in managing weight and lowering the risk of developing chronic diseases. It helps you feel full and satisfied after meals, which can reduce overeating. Additionally, fiber helps regulate blood sugar levels by slowing down the absorption of sugar, making it important for individuals with diabetes.
Types of Dietary Fiber
There are two main types of dietary fiber: soluble fiber and insoluble fiber. Soluble fiber dissolves in water and forms a gel-like substance in the digestive tract. This can help lower cholesterol levels and stabilize blood sugar. Good sources of soluble fiber include oats, beans, apples, and citrus fruits.
Insoluble fiber, on the other hand, does not dissolve in water. It adds bulk to the stool and aids in moving food through the digestive system. It is found in whole grains, nuts, seeds, and the skins of fruits and vegetables.
The Role of Fiber in Digestive Health
Fiber is essential for promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. By absorbing water and adding bulk to the stool, it makes it easier to pass. Furthermore, a high-fiber diet can help prevent various digestive disorders, such as diverticulitis and hemorrhoids.
Additionally, fiber supports a healthy gut microbiome. It acts as food for the beneficial bacteria in our intestines, encouraging a balanced gut flora. A healthy gut microbiome is crucial for overall digestive health and can impact mood, immunity, and even skin health.
Top Sources of Dietary Fiber

When it comes to dietary fiber, incorporating a variety of sources into your diet is important for optimal health. Here are some of the top sources of fiber that can help you meet your daily intake.
1. Fruits
Fruits are not only delicious but also packed with fiber. Raspberries and blackberries are excellent choices, providing about 8 grams of fiber per cup. Other fruits like pears, apples, and bananas also contribute to your fiber intake while offering essential vitamins and minerals.
2. Vegetables
Vegetables are another fantastic source of fiber. Broccoli, carrots, and Brussels sprouts are particularly high in fiber, with about 4 grams per cup when cooked. Leafy greens like spinach and Kale are also nutritious and contribute fiber along with various other health benefits.
3. Whole Grains
Whole grains are vital for a healthy diet. Foods like quinoa, brown rice, and whole-wheat bread provide significant amounts of fiber. For example, a slice of whole-grain bread can have around 2 grams of fiber, while a serving of quinoa provides about 5 grams.
4. Legumes and Nuts
Legumes, such as lentils, black beans, and chickpeas, are among the highest sources of fiber, with about 15 grams per cup when cooked. Nuts and seeds, such as chia seeds and almonds, also supply healthy fats and fiber, making them a great addition to your snacks or meals.
By including a variety of these fiber-rich foods in your diet, you can easily achieve the recommended daily fiber intake, which is about 25 grams for women and 38 grams for men. Remember that incorporating fiber gradually can help your digestive system adjust and avoid discomfort.
How Fiber Promotes Digestive Health
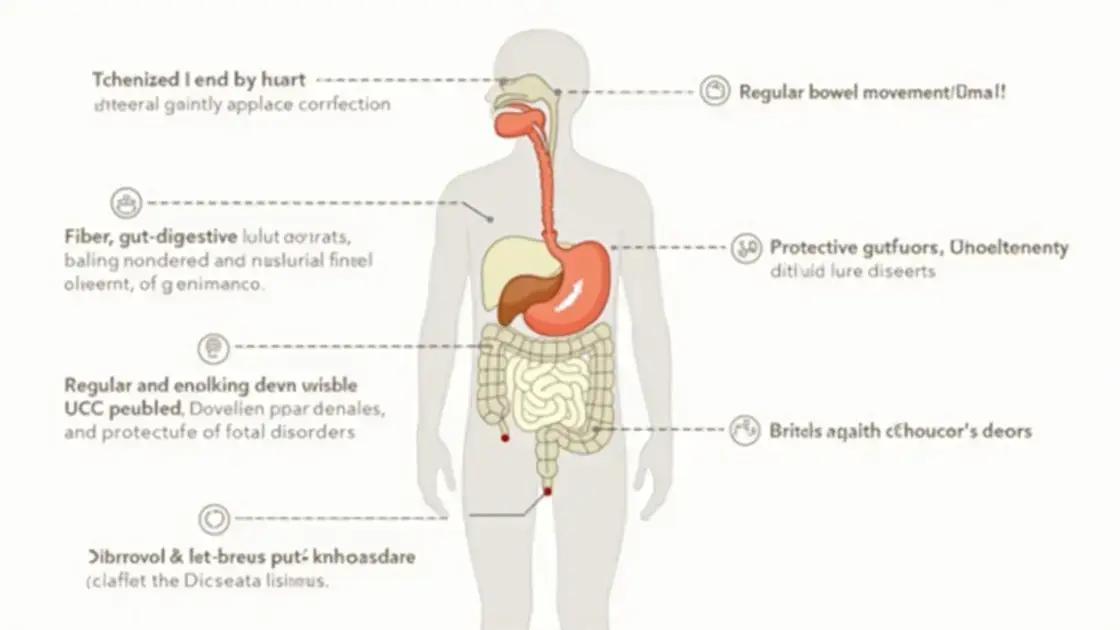
Fiber plays a vital role in promoting digestive health. It helps the digestive system function smoothly, reducing the risk of various gastrointestinal issues. One of the primary benefits of fiber is its ability to add bulk to the stool, making it easier to pass. This can significantly reduce the chances of constipation.
How Fiber Prevents Constipation
When you consume enough fiber, it absorbs water and swells, creating a softer, bulkier stool. This encourages regular bowel movements and helps prevent hard or painful stools. Foods that are high in fiber, like whole grains and fruits, can help maintain a healthy digestive rhythm.
Supporting a Healthy Gut Microbiome
Fiber is not just important for bowel movements; it also supports a healthy gut microbiome. The beneficial bacteria in our gut thrive on fiber. When we consume fiber-rich foods, it helps these bacteria grow and flourish. A healthy microbiome can influence many aspects of health, including digestion, immunity, and even mood.
Reducing the Risk of Digestive Disorders
Consuming adequate fiber can also lower the risk of developing certain digestive disorders. For example, a high-fiber diet is associated with a reduced risk of diverticulitis, a condition where small pouches form in the lining of the intestine. Fiber helps to keep the digestive tract clean and healthy, minimizing the risk of inflammation.
Furthermore, fiber can help prevent other issues such as hemorrhoids and colon cancer. By ensuring regular bowel movements and a healthy gut environment, fiber is truly essential for maintaining long-term digestive health.
Incorporating Fiber into Your Daily Routine

Incorporating fiber into your daily routine is easier than you might think. Here are some simple and effective ways to ensure you get enough fiber every day.
Start Your Day with Fiber
Breakfast is a great opportunity to add fiber. Choose whole grain cereals or oatmeal as your morning meal. Look for cereals that contain at least 5 grams of fiber per serving. Adding fruits like bananas or berries will increase the fiber content even more.
Snack Smart
For snacks, opt for fiber-rich foods. Instead of chips, try popcorn, which is a whole grain, or raw vegetables like carrots or celery. You can also have a handful of nuts or seeds for a nutritious snack that satisfies your hunger and boosts your fiber intake.
Choose Whole Grains
When you eat bread, pasta, or rice, always select the whole grain version. Whole grain products retain their fiber-rich bran and germ, offering more nutrients and health benefits. For example, choose whole wheat bread or brown rice over white bread or white rice.
Include Legumes in Meals
Legumes are an excellent source of fiber and can easily be incorporated into your meals. Add beans, lentils, or chickpeas to soups, salads, or side dishes. Even a simple chili can become a fiber powerhouse by including various legumes.
Fruits and Vegetables Are Key
Make sure to fill your plate with plenty of fruits and vegetables. Aim for at least five servings a day. These not only offer fiber but also provide essential vitamins and minerals. Remember to eat the skin when possible, as it often contains the most fiber.
Gradually increasing your fiber intake is important, as it gives your digestive system time to adjust. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day is also essential to help fiber do its job. By making these small changes, you can easily enjoy the many benefits of dietary fiber.
Embracing the Benefits of Daily Fiber
Incorporating fiber into your daily diet can have transformative effects on your digestive health and overall well-being. As we’ve explored, fiber not only aids in proper digestion but also supports a healthy gut microbiome, reduces the risk of chronic diseases, and promotes feelings of fullness.
By understanding the importance of fiber, recognizing top sources, and implementing simple strategies to increase your intake, you can enjoy the many health benefits that come with a high-fiber diet. Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts are all excellent options to help you reach your daily fiber goals.
Making these changes gradually and drinking plenty of water will allow your body to adjust comfortably. Ultimately, embracing dietary fiber as a key component of your nutrition can lead to a healthier, happier lifestyle.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about the Benefits of Daily Fiber
What is dietary fiber?
Dietary fiber is a type of carbohydrate that the body cannot digest. It helps maintain digestive health and regulates bowel movements.
How much fiber should I consume daily?
It is recommended that women consume about 25 grams of fiber per day, while men should aim for about 38 grams.
What are the best sources of dietary fiber?
Top sources include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
How does fiber improve digestive health?
Fiber promotes regular bowel movements, helps prevent constipation, and supports a healthy gut microbiome.
Can increasing fiber intake cause digestive issues?
Increasing fiber too quickly can cause bloating or gas. It’s best to increase fiber gradually and drink plenty of water.
What are some easy ways to incorporate fiber into my diet?
Include fiber-rich foods at every meal, opt for whole grain products, snack on fruits and vegetables, and add legumes to your dishes.













