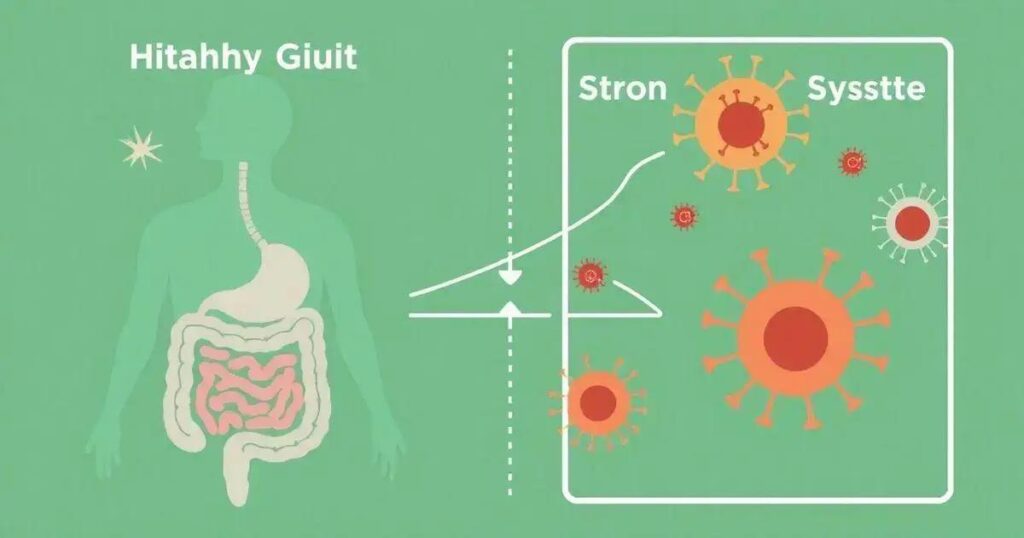
The link between gut health and immune system function is significant, as a balanced gut microbiome enhances immune responses, helping the body to fight infections. Practical tips for maintaining optimal gut health include eating diverse foods, incorporating fermented items, staying hydrated, managing stress, and exercising regularly.
The link between gut health and immune system function is gaining recognition in the medical community. Recent studies reveal that our gut microbiome plays a significant role in shaping our immune response. By understanding how these two systems interact, we can improve our overall health and immunity. Throughout this article, we will explore the fundamentals of gut health, the role of the gut microbiome in immune function, and practical tips for maintaining a healthy gut.
Understanding Gut Health
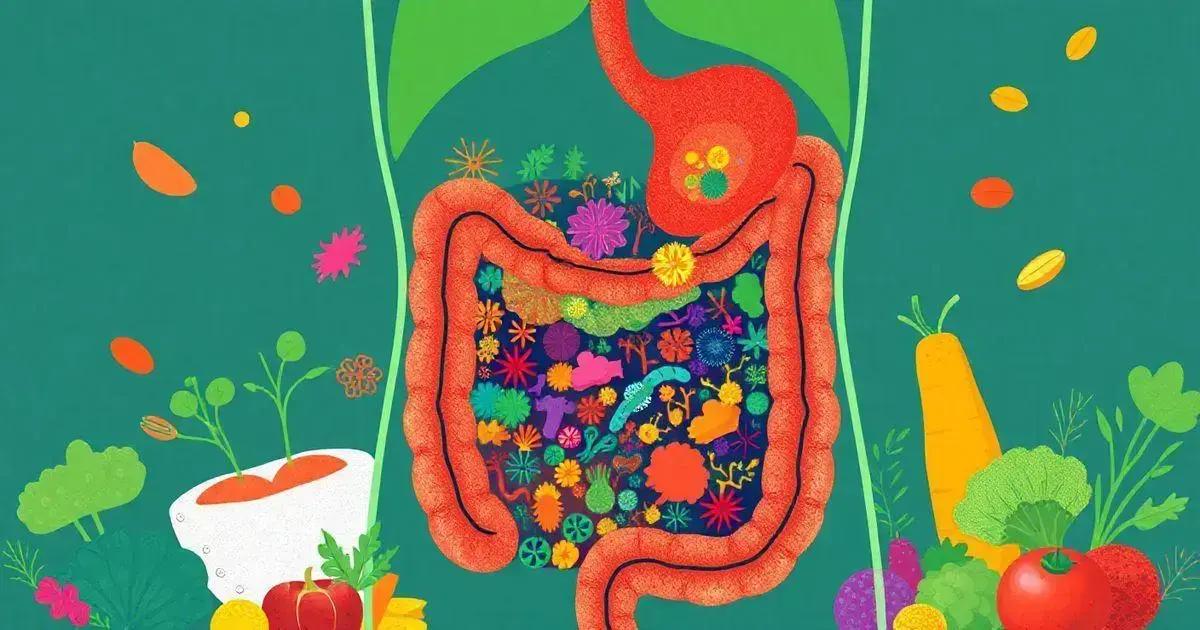
Understanding gut health is essential for maintaining overall well-being. The gut is not just responsible for digestion; it plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including the immune system. A healthy gut consists of a balanced community of microorganisms that help digest food, produce vitamins, and protect against harmful pathogens.
The Importance of Gut Microbes
Gut microbes, or gut microbiota, are tiny organisms living in our digestive system. These include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes that work together to keep our body functioning well. A diverse and balanced microbiome is vital for optimal gut health. When the balance of these microbes is disrupted, it can lead to issues such as inflammation, allergies, and even autoimmune disorders.
Factors Affecting Gut Health
Several factors can impact gut health, including diet, lifestyle, and medication use. Consuming a diet high in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods can support a healthy microbiome. On the other hand, a diet rich in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can negatively affect gut health.
Both stress and lack of sleep can also play a role. Chronic stress may alter the gut microbiota, leading to digestive problems. Thus, adopting healthy habits is essential for maintaining gut health.
How Gut Health Interacts with Other Bodily Systems
Gut health is linked to various bodily systems, especially the immune system. The gut houses a significant portion of the immune cells in the body. This connection highlights the importance of gut health not just for digestion but for the body’s overall defense mechanism.
When we maintain gut health, we boost our immune system. A balanced microbiome can promote the production of anti-inflammatory substances and help regulate immune responses.
To wrap up, understanding gut health is vital for ensuring overall wellness. By focusing on maintaining a healthy gut, we can support our immune system and improve our quality of life.
The Role of Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome is a complex community of microorganisms that live in our digestive tract. These tiny organisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, play an essential role in our health. They help digest food, produce essential nutrients, and even influence our immune system.
Functions of the Gut Microbiome
One of the primary functions of the gut microbiome is to aid digestion. They help break down complex carbohydrates and fibers that our bodies cannot digest on their own. As a result, they produce short-chain fatty acids, which are crucial for gut health.
In addition to digestion, gut bacteria produce vitamins like B vitamins and vitamin K. These vitamins are vital for metabolism and blood clotting, respectively.
Impact on the Immune System
The gut microbiome also plays a significant role in regulating our immune system. About 70% of our immune cells are located in the gut. The beneficial bacteria in our gut help educate these immune cells, teaching them how to respond to potential threats such as pathogens.
An imbalance in the gut microbiome can lead to increased inflammation and a weakened immune response. Disruptions can come from poor diet, stress, and antibiotics, all of which can harm healthy bacteria and allow harmful bacteria to thrive.
Connection to Mental Health
Interestingly, the gut microbiome is connected to mental health as well. The gut-brain axis is a communication pathway between the gut and the brain. Research indicates that certain gut bacteria can influence mood and behavior through the production of neurotransmitters.
For example, the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that helps regulate mood, primarily occurs in the gut. When the microbiome is healthy, it can support mental well-being.
Factors Affecting the Gut Microbiome
Diet plays a critical role in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. Consuming a variety of foods, particularly those high in fiber, can promote diversity within the microbiome. Fermented foods, such as yogurt and kimchi, provide beneficial bacteria that can enhance gut health.
Other factors, such as age, lifestyle, and medications, can also impact the gut microbiome. Understanding these factors is essential for maintaining a balanced microbiome.
Gut Health’s Impact on Immunity
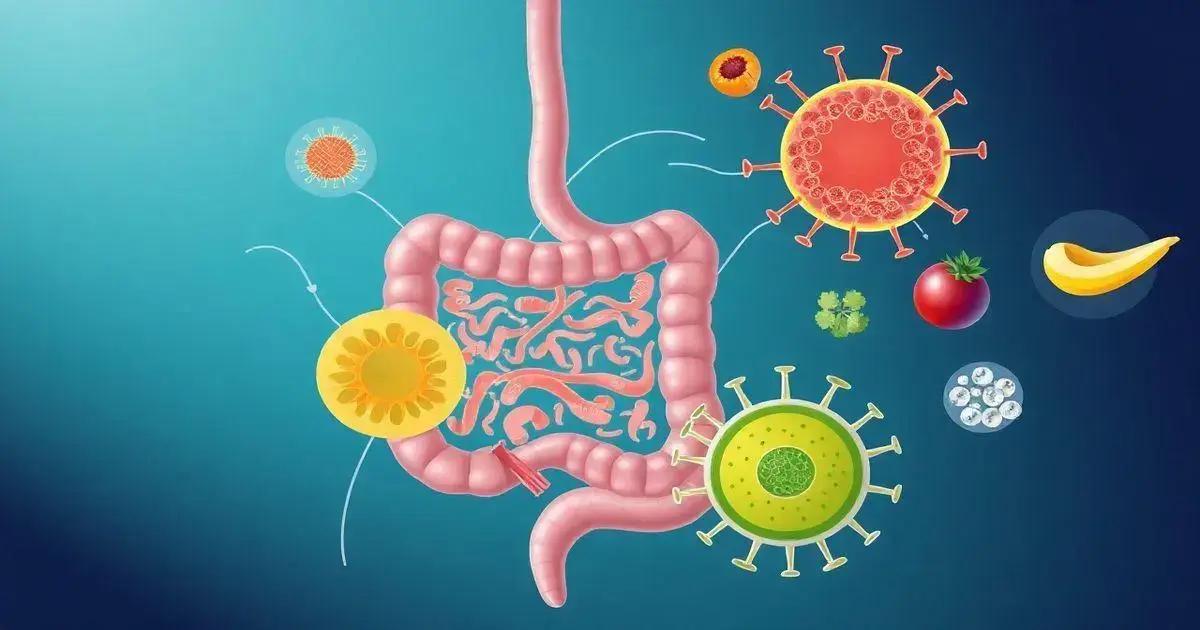
Gut health is closely tied to the immune system. The gut is home to a vast number of immune cells that help protect the body from infections and illnesses. Maintaining a healthy gut can boost your immune response and enhance your ability to fight off diseases.
How Gut Health Influences Immunity
The gut microbiome produces various compounds that affect immune function. For instance, beneficial bacteria produce substances that can help regulate inflammation in the body. When the gut microbiome is balanced, these substances promote a healthy immune response. Conversely, an unhealthy microbiome can lead to inflammation and a compromised immune system.
Furthermore, when the gut lining is functioning correctly, it acts as a barrier that prevents harmful substances from entering the bloodstream. A damaged gut lining can allow toxins and pathogens to leak into the bloodstream, triggering an immune response and causing various health issues.
Gut Flora and Immune Regulation
Gut flora also plays a significant role in educating the immune system. Good bacteria interact with immune cells and help them recognize what is harmful and what is not. This training is crucial for preventing allergic reactions and autoimmune diseases.
Research shows that people with more diverse gut microbiomes tend to have stronger immune systems. A diverse range of bacteria can help better train immune cells, improving their efficiency in combating infections.
Connection to Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is linked to various diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. A healthy gut microbiome can help control inflammation. When harmful bacteria dominate the gut, they can produce toxins that increase inflammation.
Maintaining a balanced and healthy gut can reduce inflammation levels, thus lowering the risk of these diseases. This is why focusing on gut health can have a direct impact on overall health and immunity.
Food Choices that Support Gut and Immune Health
What you eat can significantly affect your gut health. Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and probiotics can help support a healthy microbiome. These foods provide the nutrients and beneficial bacteria needed to keep your gut in balance.
On the other hand, diets high in sugar and processed foods can disrupt gut health. This can lead to an imbalance in the microbiome, which may weaken your immune system.
Practical Tips for Optimal Gut Health

To achieve optimal gut health, consider the following practical tips that can promote a balanced microbiome and improve overall well-being.
1. Eat a Diverse Range of Foods
A varied diet is crucial for gut health. Different foods provide different types of fibers and nutrients that support a diverse microbiome. Aim to include a mix of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in your meals.
2. Include Fermented Foods
Fermented foods are rich in probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria for your gut. Incorporate items like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, or kombucha into your diet. These foods can help replenish healthy gut bacteria.
3. Stay Hydrated
Drinking enough water is important for maintaining gut health. It helps in digestion and the movement of food through your gastrointestinal tract. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water a day.
4. Limit Processed Foods and Sugar
High amounts of sugar and processed foods can negatively affect gut health. These foods can lead to an imbalance in gut bacteria. Try to consume whole, unprocessed foods as much as possible to maintain a healthy microbiome.
5. Manage Stress
Stress can impact gut health significantly. Practices like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and promote gut health. Taking time to relax can benefit both your mind and your gut.
6. Get Enough Sleep
Aim for 7 to 9 hours of quality sleep each night. Poor sleep can affect your gut health and immune system. Establishing a regular sleep routine can promote better overall health.
7. Exercise Regularly
Regular physical activity can benefit gut health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Activities like walking, cycling, or swimming can all contribute to a healthy gut microbiome.
8. Consider Probiotic Supplements
If you struggle to get enough probiotics from food, consider taking a probiotic supplement. Consult with a healthcare professional to choose the best option for your needs.
By following these tips, you can support your gut health, enhance your immune system, and improve your overall well-being.
In Summary: Strengthening the Link Between Gut Health and Immunity
Our exploration of the connection between gut health and immune system function highlights the critical role of the gut microbiome in maintaining overall health. A balanced gut microbiome not only supports digestion but also enhances immune response, helping to ward off illnesses and infections.
By following practical tips for optimal gut health, such as consuming a diverse diet, incorporating fermented foods, staying hydrated, managing stress, and engaging in regular exercise, you can significantly improve your gut health.
Recognizing the impact that gut health has on your immune function can empower you to make informed lifestyle choices that promote well-being. In doing so, you invest in a healthier, more resilient body.
Actively taking steps toward a balanced gut microbiome will pave the way for better health, making your gut the backbone of a strong immune system.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions About Gut Health and Immunity
What is the gut microbiome?
The gut microbiome is a diverse community of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, residing in our digestive tract that plays a vital role in health.
How does gut health affect the immune system?
Gut health influences the immune system because a balanced gut microbiome helps regulate immune responses and enhances the body’s ability to fight infections.
What foods support gut health?
Foods that support gut health include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fermented foods, and adequate hydration, as they provide essential nutrients and promote a healthy microbiome.
Can stress impact gut health?
Yes, chronic stress can negatively impact gut health by altering gut bacteria composition and leading to digestive issues, highlighting the importance of stress management.
What lifestyle changes can improve gut health?
To improve gut health, consider eating a varied diet, including fermented foods, staying hydrated, managing stress, getting enough sleep, and exercising regularly.
Are probiotics helpful for gut health?
Yes, probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can enhance gut health, especially when obtained from fermented foods or supplements.